Highway Network Video/Event Monitoring System
 |
System Introduction |
By scientifically deploying intelligent sensing cameras, combining point, line, and area methods, real-time collection of vehicle characteristic data, traffic flow data, traffic incident information, and road segment operation status information is achieved. This constructs an intelligent road network monitoring network, creating powerful full-network perception capabilities, agile business response capabilities, in-depth data mining capabilities, and precise analysis and judgment capabilities.
Based on the business requirements of highway network monitoring, the system expands to include richer and more intelligent intelligent sensing capabilities for highway network monitoring, solving practical problems such as the difficulty in managing and maintaining video image resources and effectively deleting redundant information due to the current excessive monitoring footage and massive amount of information. Through intelligent sensing equipment, full video coverage is achieved for core highway business scenarios (accident-prone sections, sections in severe weather, tunnels, bridges, service areas, ramp interchanges, overload control stations, and traffic control stations), realizing intelligent perception, dynamic monitoring, travel services, and emergency command for the entire road network.
The video/event monitoring system is mainly used for monitoring and recording vehicles at intersections, key congested sections, and dangerous sections, including vehicle images, license plates, and vehicle characteristic data. Meeting user needs mainly involves capturing images of motor vehicles passing through the aforementioned road sections, recognizing vehicle license plates, collecting vehicle feature data, and setting up monitoring, comparison, and alarm functions.
 |
System Architecture |
The video surveillance system consists of front-end equipment, a transmission network, and a back-end platform. The platform has a two-tier architecture. Generally, the front-end equipment transmits directly to the municipal highway bureau's management platform for aggregation and application management. The management platform then distributes client accounts to the sub-control centers of various district and county highway bureaus for application within their authorized scope. Alternatively, the video streams from the front-end equipment can first be aggregated at the sub-control centers of the district and county highway bureaus. Each sub-control center manages the video surveillance within its own area independently, and then uploads the video data to the municipal highway bureau's management platform for monitoring. Specific details depend on local policies.
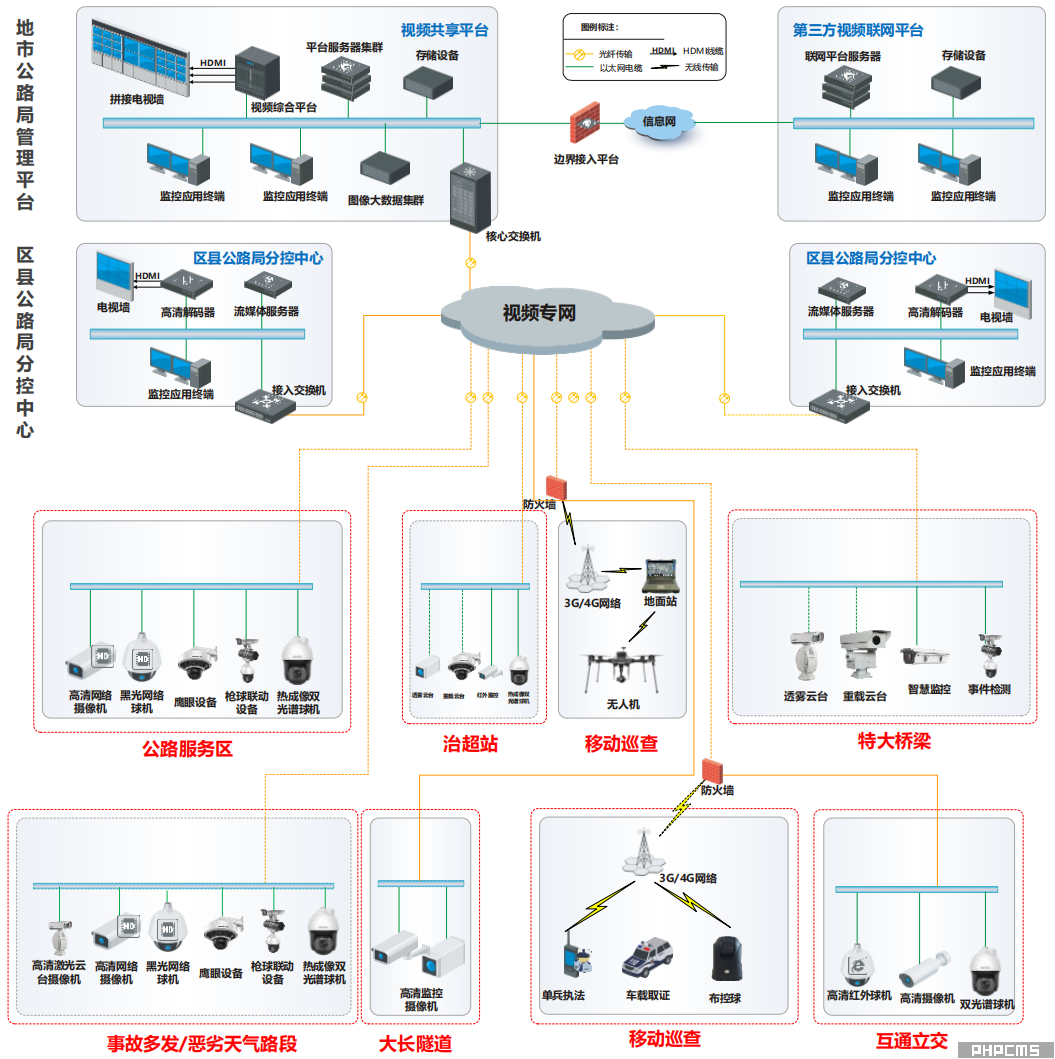
 |
System Composition |
This system generally consists of three parts: front-end equipment, transmission network, and back-end management subsystem.
Appropriate types of cameras should be deployed for different application scenarios to achieve the best video surveillance effect. The following are recommended camera types for different occasions for reference:
Accident-prone road sections and road sections in severe weather

A fixed starlight/blacklight high-definition monitoring point is set up every 500m, a dual-spectrum PTZ camera is set up every 1km, and a high-speed thermal imaging PTZ camera is set up every 3km to achieve full video coverage of the road section by combining near and far distances and high and low distances. This ensures that clear video images of the entire road section can be provided even in severe weather, and that early warning information can be issued in a timely manner to ensure smooth traffic.
Mega bridges

High-definition cameras will be deployed 100m-250m from the bridge to record and identify vehicles entering the bridge, primarily focusing on license plates and vehicle models. Radar will also be deployed to measure vehicle speed. The bridge will be monitored throughout its entire length, with a fixed starlight/blacklight camera every 500m and a thermal imaging dual-spectrum camera every 1km. Additional video monitoring points will be set up at curves. Medium-sized thermal imaging PTZ cameras are recommended, with one camera every 2km-3km.
Traffic incident detection cameras

It is recommended that one traffic incident detection camera be installed every 300 meters.
Hub Interchange

Set up 2-3 high-definition video monitoring points according to the monitoring range and angle. In accordance with the full-process monitoring mode, deploy fixed starlight/blacklight cameras on the ramps, fixed starlight/blacklight cameras at the turning points, and eagle-eye panoramic cameras at the highest points of the interchanges.
Overweight and overload detection stations and traffic control stations

Several high-definition video monitoring points, combining near and far distances and high and low elevations, are set up according to the monitoring range.
Smart highway rest stops/service areas

Several high-definition video monitoring points, combining near and far distances and high and low elevations, are set up according to the monitoring range.
Incident detection road section

The event detection system has two deployment modes. The first mode involves a backend-deployed event detection server connecting to frontend monitoring equipment to intelligently analyze the monitoring video stream, detecting traffic events and analyzing traffic flow. The second mode uses frontend-deployed event camera/PTZ camera devices to detect traffic events and analyze traffic flow in the monitored scene. The event detection system consists of frontend equipment, a transmission network, and a backend management subsystem.
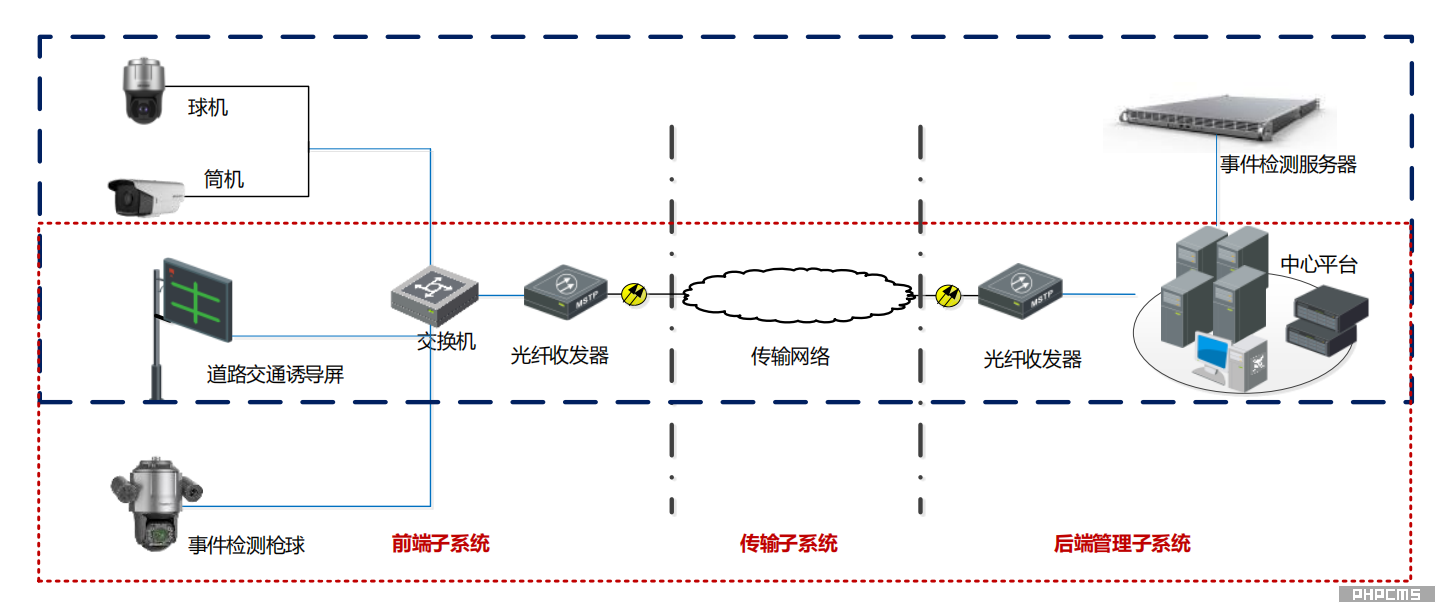
The front-end section handles image acquisition and encoding, primarily consisting of high-definition network cameras, PTZ cameras, and traffic guidance displays. The high-definition network cameras work in conjunction with the back-end event detection server to detect abnormal traffic events; the PTZ cameras primarily detect abnormal traffic events; and the traffic guidance displays are used to display traffic event and road network operation status information.
The transmission network is the data communication link, mainly utilizing the user's existing dedicated network for data transmission.
The back-end management subsystem mainly includes the event detection server and the central platform management software. The event detection server can detect various traffic events in real time, and also has traffic parameter acquisition capabilities, enabling image capture and license plate recognition of detected events. The central platform management software primarily manages the front-end devices and the event detection server, receives alarm information uploaded by the event detection server and the front-end PTZ cameras, and provides real-time event preview, data query, traffic parameter information statistics, and information dissemination functions.








